PayPal Breach 2025: Strengthen Your Passwords Now
PayPal Breach Exposes Millions: A Wake-Up Call for Password Security in 2025
The recent emergence of a cybercriminal selling allegedly 15.8 million PayPal credentials on the dark web has reignited concerns about password security and digital authentication practices. While PayPal denies a new breach occurred, attributing the data to a 2022 credential stuffing attack, this incident serves as a critical reminder of the evolving cybersecurity landscape and the urgent need for better password hygiene.
The PayPal Incident: Facts vs. Fiction
A cybercriminal using the handle “Chucky_BF” is advertising what they claim to be a “Global PayPal Credential Dump 2025” containing 15.8 million plaintext passwords and email addresses for just $750. However, cybersecurity experts and PayPal itself dispute the authenticity and timing of this data.
The company has confirmed that no new breach occurred in 2025, instead linking the data to a 2022 credential stuffing attack that compromised approximately 35,000 accounts. This earlier incident resulted from cybercriminals exploiting security vulnerabilities, including inadequate multi-factor authentication and poor access controls during the implementation of IRS Form 1099-K distribution changes.
PayPal’s security lapses during the 2022 incident were significant enough to warrant a $2 million settlement with New York State’s Department of Financial Services for violating cybersecurity regulations. The breach exposed sensitive information including full names, dates of birth, postal addresses, Social Security numbers, and tax identification numbers.
The Current State of Password Security
The alleged PayPal dataset, whether genuine or recycled, highlights broader password security challenges that affect millions globally. Current statistics reveal alarming trends in password behavior:
Weak Password Epidemic
The most common passwords remain shockingly predictable. According to NordPass’s 2024 analysis, “123456” continues to dominate as the world’s worst password, used by over 3 million people for personal accounts.
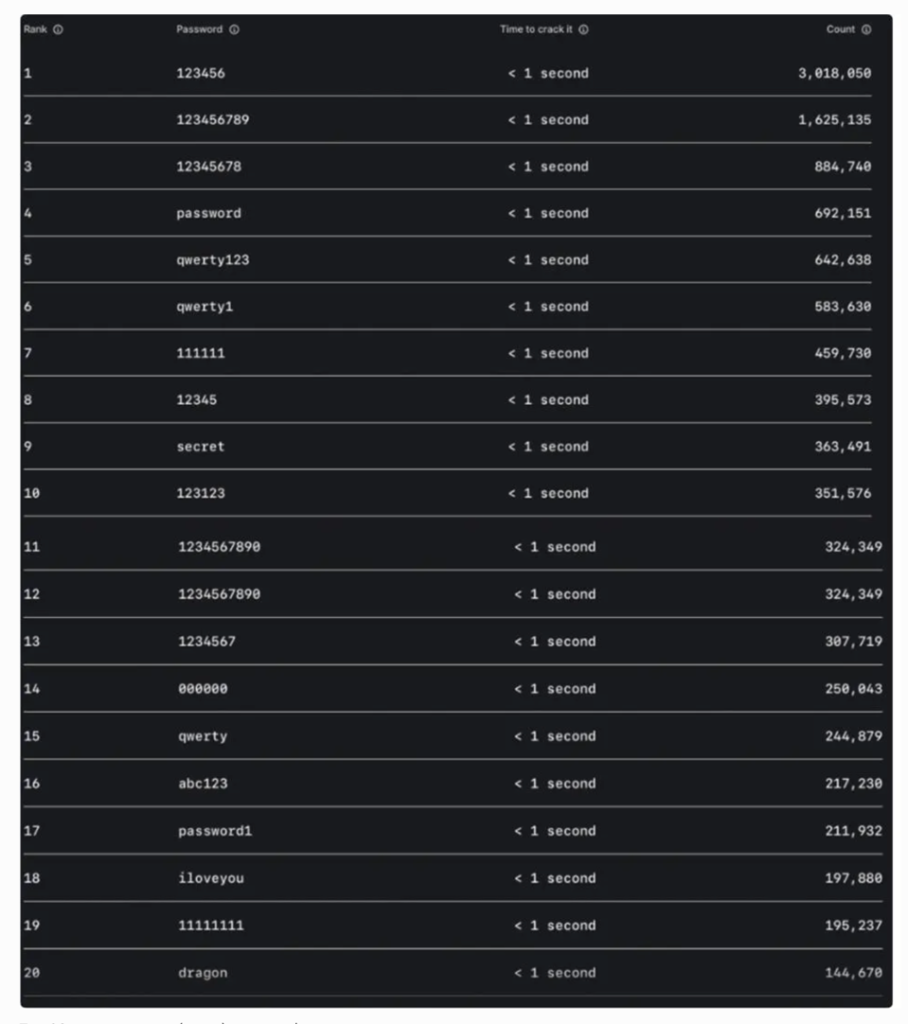
Other frequently used weak passwords include “123456789,” “password,” and simple keyboard patterns like “qwerty”. These passwords can be cracked in less than one second using modern computing power.
Password Reuse Crisis
Password reuse remains a critical vulnerability:
- 60% of Americans reuse passwords across multiple accounts
- 13% use the same password for everything
- Globally, 78% of people admit to reusing passwords
- 25% of users reuse passwords across 11-20+ accounts
Rising Authentication Challenges
The average person now manages 70-80 passwords personally, with professionals handling up to 255 passwords including work accounts. This overwhelming number contributes to poor password practices as users struggle to maintain unique, strong credentials across all accounts.
Computing Power Acceleration Threatens Password Security
The cybersecurity landscape has become dramatically more dangerous due to advances in computing power. Hive Systems’ 2025 Password Table reveals alarming trends:
- Password cracking times have decreased by nearly 20% compared to 2024
- An 8-character lowercase password can now be cracked in just 3 weeks
- AI-grade hardware has increased cracking speeds by over 1.8 billion percent compared to consumer devices
This acceleration means passwords that were secure last year could now be cracked in a fraction of the time. The same powerful hardware driving AI innovations like ChatGPT is also being leveraged by cybercriminals to break passwords at unprecedented speeds.
Multi-Factor Authentication: The Critical Defense Layer
Despite the password crisis, there’s hope in multi-factor authentication (MFA) adoption. Research consistently shows MFA’s effectiveness:
- Microsoft reports that MFA blocks 99.9% of automated attacks
- Google confirms that 2FA blocks 100% of automated bot hacks
- 57% of businesses globally have implemented MFA as of 2019, with adoption growing
However, significant gaps remain. 54% of small to medium businesses still don’t implement MFA at all, with only 28% making it mandatory. This leaves millions of accounts vulnerable to credential stuffing attacks like the one that affected PayPal in 2022.
The Rise of Passkeys: A Passwordless Future
The authentication landscape is rapidly evolving toward passwordless solutions. Passkey adoption has surged dramatically:
- 87% of organizations have deployed or are implementing passkeys, up 14 percentage points since 2022
- 74% of consumers are aware of passkeys, with 69% enabling them on at least one account
- Major platforms report substantial adoption: Google has over 800 million accounts using passkeys, while Amazon saw 175 million users create passkeys in their first year
Passkeys offer compelling advantages:
- 90% of organizations report security improvements after implementation
- 82% note positive effects on user experience
- 77% observe reduced help desk calls
- Users find passkeys 6 times faster than traditional passwords
Essential Security Recommendations
Given the current threat landscape, individuals and organizations must take immediate action:
For Individual Users:
Immediate Actions:
- Change passwords that haven’t been updated recently, especially for financial services
- Enable two-factor authentication on all critical accounts, using authenticator apps rather than SMS
- Implement passkeys wherever available for enhanced security and convenience
Long-term Security Practices:
- Use unique passwords for every account, with minimum 14-character lengths
- Employ password managers to generate and store strong, unique credentials
- Avoid personal information in passwords (names, birthdays, pet names)
- Regularly monitor accounts for unauthorized access
For Organizations:
Security Infrastructure:
- Mandate multi-factor authentication for all users, prioritizing those with access to sensitive data
- Implement rate limiting and CAPTCHA to prevent automated attacks
- Deploy passkey authentication for improved security and user experience
- Provide comprehensive cybersecurity training to all personnel
Risk Management:
- Conduct regular security audits and penetration testing
- Monitor for credential stuffing attacks and suspicious login patterns
- Establish incident response procedures for potential breaches
- Ensure compliance with relevant cybersecurity regulations
The Broader Implications
The PayPal incident, whether involving new or recycled data, underscores several critical points about modern cybersecurity:
Credential Stuffing Remains Highly Effective: The success of these attacks relies on users’ tendency to reuse passwords across platforms. When one service is breached, criminals test those credentials across hundreds of other sites.
Data Has Extended Lifespans: Even if the PayPal data stems from 2022, its appearance in 2025 demonstrates that compromised credentials maintain value for years, especially when users fail to change passwords regularly.
Security Awareness Gaps Persist: Despite decades of warnings about password security, fundamental mistakes continue to plague both individuals and organizations.
Moving Forward: A Multi-Layered Approach
The path to better security requires a comprehensive strategy combining technological solutions with behavioral changes:
Technology Integration: Organizations must accelerate adoption of modern authentication methods like passkeys while maintaining backward compatibility during transition periods.
Education and Training: Both consumer and corporate education programs need enhancement to address the growing sophistication of cyber threats.
Regulatory Frameworks: Strong cybersecurity regulations like New York’s standards help ensure organizations maintain appropriate security measures.
Industry Cooperation: The success of passkey adoption demonstrates what’s possible when major technology companies collaborate on security standards.
The alleged PayPal credential sale serves as a stark reminder that cybersecurity is an ongoing challenge requiring constant vigilance. While the specific claims about this dataset may be exaggerated or recycled, the underlying vulnerabilities it represents are very real. By implementing strong password practices, enabling multi-factor authentication, and embracing next-generation solutions like passkeys, both individuals and organizations can significantly improve their security posture in an increasingly dangerous digital landscape.
The choice is clear: continue relying on weak, reused passwords and remain vulnerable to attacks, or embrace the security tools and practices available today to build a more secure digital future. With password cracking capabilities accelerating rapidly, there’s no time to waste in making this critical transition.


